Let’s be blunt: risk management isn’t just another trading strategy. It’s the one skill that separates traders who build lasting careers from those who burn out after a few lucky (or unlucky) bets. We’ve all felt the sting of a trade gone wrong, and this guide is about turning that pain into a disciplined process. It’s the active, moment-to-moment practice of protecting your capital by deciding exactly how much you’re willing to lose before you ever enter a trade.
Without a solid handle on this, even the most brilliant trading strategy is a ticking time bomb. This isn’t about finding “guaranteed profits” — it’s about staying in the game long enough to let your strategy work.
Why Risk Management Is Your Most Important Skill
Many traders jump into the markets with a single-minded focus: finding winners. They spend all their time hunting for the perfect setup or a flawless indicator. But this approach completely ignores a painful truth that the market eventually teaches everyone: losses are an unavoidable part of the business.
Your first job isn’t to make money. It’s to protect the money you already have.
Think of it like being a seasoned mountaineer. A rookie might only fantasize about reaching the summit, but the expert’s mind is on their gear, the weather forecast, and their emergency routes. They know the mountain doesn’t care about their ambition; it has its own unforgiving rules. Survival depends not just on climbing ability, but on managing the immense risks involved.
This is the very essence of risk management in trading. It’s the disciplined practice of checking your gear (your capital), planning your route (your trade plan), and knowing exactly when to turn back (your stop-loss) before a small slip turns into a catastrophic fall.
Before we dive deeper, let’s break down the foundational pillars of risk management. Think of this table as a quick cheat sheet for the core concepts we’ll be exploring.
Core Principles of Trading Risk Management
| Principle | Why It Matters | Practical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Preservation | Your trading capital is your lifeblood. Without it, you’re out of the game entirely. | Setting a max loss per day or per week to protect your account from a death spiral. |
| Controlled Losses | Losses are inevitable. The key is to keep them small and manageable so they don’t wipe out your wins. | Using a pre-defined stop-loss on every single trade without exception. |
| Position Sizing | Determines how much you stand to lose on a single trade, directly controlling your risk exposure. | Calculating your trade size based on a small percentage of your total account (e.g., 1%). |
| Risk/Reward Ratio | Ensures your potential wins are significantly larger than your potential losses over time. | Only taking trades where the potential profit is at least 2 or 3 times the amount you’re risking. |
These principles work together to form a defensive shield, allowing you to stay in the market long enough for your skills to pay off.
The Mindset of a Professional Trader
To truly embrace risk management, you need to make a profound mental shift. You have to move from thinking, “How much can I make on this trade?” to asking, “How much can I afford to lose if I’m wrong?”
This isn’t about being scared; it’s about being realistic and professional. The markets are a game of probabilities, not certainties, and taking small, controlled losses is simply the cost of doing business. Your long-term goal isn’t to dodge losses forever — it’s to make sure they’re always small and predetermined.
This is how you survive the inevitable losing streaks and stay in the game long enough for your winning trades to compound and grow your account. Many of the world’s most successful traders live by the rule of risking only 1% to 2% of their trading capital on a single trade. It’s a simple rule that keeps their accounts safe and their emotions in check.
“The first rule of trading is to play great defense, not great offense. Every day I assume every position I have is wrong.” – Paul Tudor Jones
Ultimately, mastering risk management builds longevity. It’s the rock-solid foundation that all profitable trading is built upon, allowing you to weather the storms and be ready for the opportunities that will inevitably come your way. For more ways to build a professional mindset, check out our guide with other powerful tips for traders.
The Three Pillars of Capital Protection
Solid risk management isn’t a single trick or a magic bullet. It’s a set of disciplined habits built on a few core ideas — a defensive structure that shields your capital from those gut-wrenching, account-ending blows. This structure lets you take the inevitable hits, learn from them, and stay in the game long enough to win.
Everything rests on three fundamental pillars that work together to keep you trading tomorrow.
This infographic lays out the hierarchy of capital protection, showing how these three pillars form the bedrock of any sound risk management strategy.
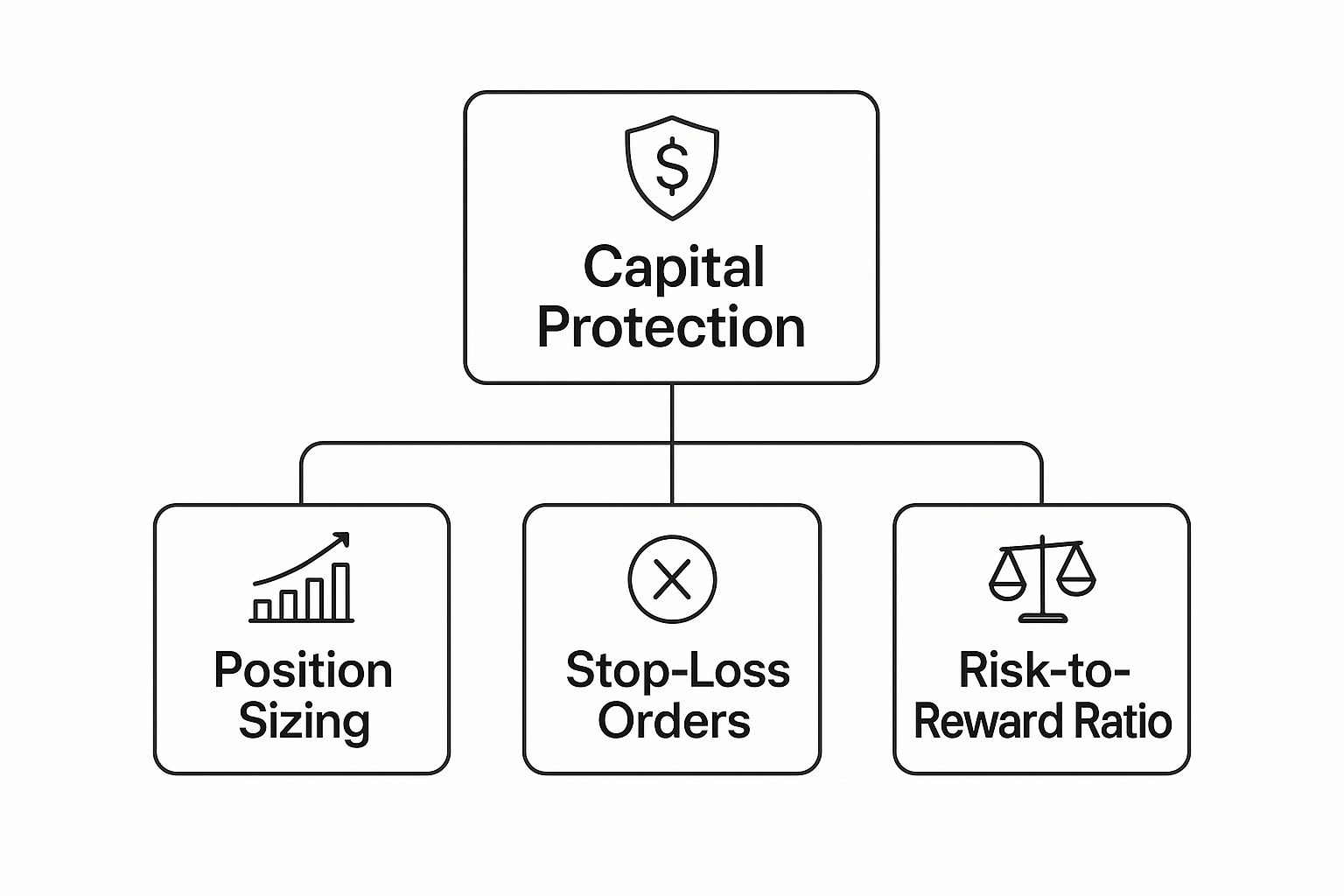
As you can see, Position Sizing, Stop-Loss Orders, and the Risk-to-Reward Ratio are the non-negotiables. Let’s break down exactly why.
Pillar 1: Position Sizing
Position sizing answers the most critical question you’ll ask before every single trade: “How much?” It’s the art of figuring out the right number of shares or contracts to trade based on your account size and, more importantly, how much you’re willing to lose if you’re wrong.
This is your ultimate defense against blowing up your account.
A huge mistake many traders make is using a fixed size, like buying 100 shares of every stock. This is a one-way ticket to disaster. Why? Because the risk on a volatile $10 stock is worlds apart from a stable $200 stock.
A fantastic guideline to live by is the “1% Rule.” Put simply, you should never risk more than 1% of your total account equity on any single trade.
Practical Example: For a trader with a $10,000 account, this means the maximum loss you’ll accept on one trade is $100. This rule is like a firewall; even a brutal string of ten straight losses would only draw your account down by about 10%, not wipe you out completely. This provides the breathing room needed to recover.
This simple math takes your ego and greed out of the driver’s seat. It forces you to play defense first, long before you even start dreaming about the profits.
Pillar 2: Stop-Loss Orders
A stop-loss order is your escape plan — your pre-defined exit if a trade goes sour. It’s an automated order you place with your broker to sell a security the moment it hits a specific price. Think of it as the eject button in a fighter jet; its only job is to get you out of a dangerous situation before it becomes fatal.
We’ve all been there: holding a losing trade, just hoping and praying it turns around. A stop-loss is a tool designed to short-circuit that exact emotional trap by making the exit decision for you when you are clear-headed, not when you are stressed.
But a stop isn’t just a random price. It should be placed at the logical point where your original trade idea is proven wrong. For example, if you buy a stock because it found strong support at $50, your stop-loss might sit just below that level at $49.50. If the price breaks that support, your reason for being in the trade is gone, and the stop automatically gets you out for a small, controlled loss.
- For a long (buy) trade: The stop-loss goes below your entry price, often tucked under a key support level.
- For a short (sell) trade: The stop-loss goes above your entry price, usually just over a key resistance level.
Using a stop-loss on every trade is a non-negotiable rule for disciplined traders. It turns risk from a scary, unknown monster into a calculated, manageable number.
Pillar 3: Risk-to-Reward Ratio
This final pillar ties the first two together. It ensures the wins you do get are actually worth the risks you took to get them. The risk-to-reward ratio simply compares the money you’re risking (the distance from your entry to your stop-loss) to your potential profit (the distance to your take-profit target).
You’ll often see it written as a ratio, like 1:2 or 1:3. A 1:3 risk-to-reward ratio means you’re risking $1 for the potential to make $3.
This concept is a game-changer because you don’t need a crazy-high win rate to be profitable. In fact, many professional traders win on fewer than 50% of their trades. Their secret? Their winners are significantly bigger than their losers, allowing them to be profitable over the long term.
Let’s imagine you risk $100 on every trade:
- Scenario A (Poor Risk/Reward): You aim for a 1:1 ratio. After 10 trades, you have 6 winners (+$600) and 4 losers (-$400). Your net profit is $200.
- Scenario B (Good Risk/Reward): You aim for a 1:3 ratio. After 10 trades, you have only 4 winners (+$1200) and 6 losers (-$600). Your net profit is $600.
Look at that. Even with a lower win rate, the trader in Scenario B made three times more money. This proves the power of prioritizing trades where the upside massively outweighs the manageable downside. That kind of long-term thinking is the hallmark of a pro.
Calculating Your Position Size The Right Way

Knowing the theory behind risk management is one thing. Actually putting it to work is where true trading discipline is built. It all boils down to turning a concept like the “1% Rule” into a concrete action.
Calculating your position size is the single most important step you can take to make sure one bad trade doesn’t blow up your account. It’s not about complex algebra; it’s about simple, repeatable math that acts as a guardrail against your own emotions.
When you figure out your position size before you click the buy button, you take greed and fear out of the driver’s seat. It all comes down to three things you should already know: your total account size, your risk percentage, and where you’re placing your stop-loss.
The Position Size Formula
This is the calculation that should be at the heart of every single trade you take. It connects what you have with what you’re willing to lose, giving you the exact trade size that respects your rules.
Position Size = (Account Size x Risk Percentage) / (Entry Price – Stop-Loss Price)
This simple equation tells you precisely how many shares or units to trade while keeping your potential loss locked at a level you’re comfortable with. It’s a universal tool that works for stocks, forex, crypto — you name it.
Your position size should be different for almost every trade because your stop-loss distance will always vary. This is the secret sauce of smart, adaptive risk management.
Let’s run through a quick example to see how this works in the real world.
Applying The Formula: A Real-World Scenario
Let’s say you have a $5,000 trading account. You stick to the 1% rule, which means the absolute most you’re willing to lose on a single trade is $50 ($5,000 x 0.01).
You’ve spotted a potential setup in a stock, let’s call it XYZ Corp.
- Your planned entry price: $100.00
- Your planned stop-loss: $98.00 (you found a solid support level there)
- The risk per share is: $100.00 – $98.00 = $2.00
Now, we just plug those numbers into our formula:
Position Size = ($5,000 Account x 0.01 Risk) / ($100.00 Entry – $98.00 Stop)
Position Size = $50 / $2.00
Position Size = 25 shares
And there it is. To risk exactly $50 on this specific trade, you can only buy 25 shares of XYZ. If the trade turns against you and hits your stop, you lose a predictable and completely manageable $50. No surprises.
Of course, this all hinges on putting your stop in the right place. You can learn more about that in our guide on how to set stop-losses.
Why Consistency Is Everything
Here’s where many traders go wrong. They get into a habit of trading the same size on everything. Imagine if you just decided to buy 100 shares of every stock, no matter the setup.
With the XYZ trade, buying 100 shares at a $2.00 risk per share means you’re actually risking $200 (100 shares x $2.00). That’s 4% of your $5,000 account, completely shattering your risk plan. That isn’t trading; it’s gambling.
By calculating your position size every single time, you normalize your risk. It doesn’t matter if your stop is tight or wide; your potential dollar loss stays the same. This is the discipline that separates professionals from hobbyists and builds a lasting career in the markets.
Here’s a quick table to illustrate how your stop-loss distance dramatically changes your position size, even when your risk stays constant at 1%.
Position Size Examples for a $10,000 Account (1% Risk)
This table shows how a tighter or wider stop-loss directly impacts how many shares you can buy while keeping your risk at a steady $100 per trade.
| Asset | Entry Price | Stop-Loss Price | Risk per Share/Unit | Maximum Position Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stock A | $50.00 | $49.00 | $1.00 | 100 Shares |
| Stock B | $200.00 | $195.00 | $5.00 | 20 Shares |
| Stock C | $25.00 | $24.50 | $0.50 | 200 Shares |
| Forex Pair | 1.1200 | 1.1150 | $0.0050 | 20,000 Units |
Notice how a smaller risk per share (like in Stock C) allows for a much larger position, while a wider stop (like in Stock B) forces a smaller one. The goal is always the same: keep the potential loss at $100. This is risk management in action.
Navigating The Modern Risk Landscape
Your risk management plan is only as good as your awareness of what’s happening outside your charts. The market doesn’t exist in a bubble; it’s a living, breathing thing that reacts to global events at lightning speed. A perfect technical setup can get completely wiped out by a single headline.
This is the modern risk landscape. It’s a tangled web of interconnected factors where geopolitical tensions, surprise economic reports, and sudden shifts in sentiment can spark massive, unpredictable price swings. Ignoring these outside forces is like trying to sail a ship by only looking at your compass, totally oblivious to the hurricane barreling down on you.
We’ve all seen it happen. A surprise inflation report drops, and in seconds, a quiet market turns into absolute chaos. Or a conflict overseas escalates overnight, sending shockwaves through commodities and currencies. These aren’t just little blips on the screen — they are fundamental shifts in risk that can blindside even the most disciplined traders.
The Rise of Algorithmic Trading
Adding another layer to this complexity is the sheer dominance of high-frequency and algorithmic trading. These are automated computer programs that execute trades at speeds no human can match, and they often amplify market moves. When a big news event hits, thousands of these algorithms can react at the exact same moment, causing price swings that are faster and more extreme than ever before.
This means you have far less time to react. What might have been a gentle dip a decade ago can now become a flash crash in a matter of minutes. Solid risk management trading in today’s environment means you have to respect this new dynamic and its potential for sudden, explosive volatility.
“In today’s markets, risk isn’t just about being wrong on a trade. It’s about being right, but at the wrong time. An unforeseen event can turn a winning position into a catastrophic loss before you can even react.”
Developing Situational Awareness
So, how do you stay informed without drowning in the 24/7 noise from financial media? The goal isn’t to become a political expert or an economist. It’s about developing a practical awareness of the scheduled events that are known market movers.
This is where a simple tool becomes your best friend: an economic calendar. This is a schedule that lists all the major upcoming economic announcements, like:
- Interest Rate Decisions: Central bank meetings are huge drivers of volatility, especially for currency and bond markets.
- Inflation Reports (CPI/PPI): These numbers have a massive impact on market expectations and what central banks will do next.
- Employment Data: Reports like the Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP) in the U.S. can cause huge swings across every asset class.
- GDP Figures: These give a broad snapshot of an economy’s health, directly influencing investor mood.
The modern trading world is heavily swayed by things that go way beyond technical indicators. In fact, research from Aon’s global risk management survey shows that geopolitical and macroeconomic risks now top the list of concerns for global firms, with economic slowdown ranking as a major worry. This is all driven by trade tensions, inflation, and political instability — any of which can abruptly crush asset prices and liquidity.
By knowing when these events are coming, you can make a conscious choice: tighten your stops, cut your position size, or just stay on the sidelines and avoid the mess altogether. This proactive approach turns an unknown external threat into a variable you can actually manage. It’s a vital step toward becoming a more adaptable and resilient trader.
Mastering The Psychology of Risk

You can have the most dialed-in formulas for position sizing and stop-losses, but they’re useless if your emotions hijack the controls. When it comes down to it, the biggest and most unpredictable risk in your trading career isn’t the market — it’s you. Getting a handle on your own psychology is absolutely non-negotiable for effective risk management trading.
The market is a relentless psychological battlefield. It feels perfectly engineered to trigger our deepest instincts of fear and greed, which are almost always the wrong response at the wrong time. A solid trading plan is your shield, but your own cognitive biases — mental shortcuts that can lead to errors in judgment — are the saboteurs trying to tear it down from the inside.
We’ve all been there. That frantic urge to chase a trade that’s already skyrocketing, or the stubborn refusal to cut a loser because “it has to come back.” These aren’t signs of a bad strategy; they’re just signs of being human.
The Two Demons of Trading Psychology
Two powerful mental traps are responsible for more blown accounts than any market crash. Simply recognizing them is the first step toward disarming their power over your decisions.
First up is the Fear of Missing Out (FOMO). This is that gut-wrenching anxiety you feel watching an asset soar without you, compelling you to abandon your rules just to get in on the action. Trading on FOMO is a classic recipe for buying at the absolute top, right before the inevitable reversal leaves you holding an immediate, unplanned loss.
The second demon is Loss Aversion. This sneaky cognitive bias makes the pain of a loss feel roughly twice as intense as the pleasure of an equal gain. It’s the voice in your head that convinces you to hold a losing trade, bending your rules and praying for a turnaround. This is how a small, manageable loss snowballs into a devastating one — all to avoid the sting of being wrong.
A disciplined trader treats small losses as a business expense. An emotional trader avoids small losses at all costs, and in doing so, invites catastrophic ones.
Conquering these impulses takes more than just willpower. It requires a structured, deliberate approach to building emotional discipline.
Forging Emotional Discipline
Your mind is a tool. And like any tool, it needs to be maintained and sharpened. Building emotional discipline is an active, ongoing process, not a one-time fix. Here are a few battle-tested techniques to keep your psychology from wrecking your risk management.
- Keep a Detailed Trading Journal: Think of this as your psychological mirror. By logging not just your trades but your emotions before, during, and after, you’ll start to see patterns. Did you enter out of boredom? Hold a loser out of pure hope? A journal makes your emotional triggers visible, turning vague feelings into hard data you can actually use.
- Implement a Pre-Trade Routine: Consistency is the bedrock of discipline. Create a simple checklist you must follow before every single trade. Does the setup meet all your criteria? Is your position size correct? Is your stop-loss already in place? This simple ritual creates a buffer between an emotional impulse and the “buy” button, forcing a moment of logical reflection.
- Know When to Walk Away: Sometimes the best trade you can make is no trade at all. Set hard-and-fast rules for stopping, like a maximum loss per day or a limit of consecutive losing trades. This is your defense against “revenge trading” — that desperate scramble to win back money you just lost. Walking away protects your capital and, just as importantly, your mental state for the next session.
Mastering your mindset is a journey, not a destination. It’s all about understanding how your emotional reactions directly impact your bottom line. By using tools like an equity curve simulator, you can visualize how disciplined risk management — free from emotional swings — leads to more stable, long-term growth. This is the final, crucial piece of the risk management puzzle.
Building Your Personal Risk Management Plan
All the theory and formulas are great, but they don’t mean a thing until you turn them into a concrete, personal plan. This isn’t about grabbing some generic template online. It’s about creating a living document — a set of non-negotiable rules you build around your own goals, your trading style, and yes, your emotional triggers.
Think of this plan as the constitution for your trading business. You write it when you’re calm and clear-headed so that when the market gets chaotic and your emotions are running high, you don’t have to think. You just have to follow your own rules. This is what risk management in trading is all about.
The process of building this plan forces you to answer the hard questions before you put a single dollar on the line. It’s the final, crucial step in shifting from a reactive, emotional trader to a proactive, disciplined one.
Essential Components of Your Plan
Your personal risk management plan needs to be clear, concise, and something you can glance at in a second. It doesn’t have to be a novel, but it absolutely must be specific. Here are the core pillars every trader needs to define:
- Maximum Risk Per Trade: The classic 1% rule is a fantastic starting point, but you need to decide what’s right for your account and your nerves. Write it down: “I will never risk more than 1% of my account on any single trade.”
- Maximum Daily Loss: This is your circuit breaker — the point where you walk away, no questions asked. For example, “If my account balance drops by 3% in one day, I’m done. I’ll close all positions and shut it down.”
- Maximum Weekly Loss: This rule is your safeguard against a nasty, prolonged drawdown that can wreck your account and your confidence. A good rule might be, “If my account is down 6% for the week, I stop trading completely until the following Monday.”
These hard limits are your best defense against the “death by a thousand cuts” that takes out so many traders. They protect your capital, but just as importantly, they protect your mental energy.
Defining Your Trading Rules
Beyond the numbers, your plan needs to spell out your rules of engagement — the “how” and “why” behind your trades. This is all about removing guesswork and preventing you from talking yourself into bad decisions in the heat of the moment.
Your trading plan is your objective boss. It tells you what to do, removing your emotional self from the decision-making process when you are most vulnerable.
Make sure to include specific rules for:
- Entry Criteria: What exact setup or signal must be present before you even think about entering a trade?
- Exit Criteria (for Profits): How do you take profits? Is it a fixed price target, or do you use a trailing stop to let winners run?
- Stop-Loss Placement: Where does your stop-loss go every single time based on your strategy? No exceptions.
This isn’t just for retail traders. We’re seeing risk become the new normal across the board. The commodity trading world, for instance, recently saw volatility margins drop by over 20%, but they’re still double what they were in the 2010s. It’s a clear signal that even in “normalizing” markets, having a rock-solid risk framework is non-negotiable for survival. You can dig deeper into these commodity trading risk insights at OliverWyman.com.
Your plan is your personal commitment to discipline. Write it down, read it every day before the market opens, and never, ever break your own rules. This document will become the foundation of your long-term survival and success as a trader.
Common Questions Answered
Even with the best plan, you’re going to have questions. Let’s tackle some of the most common ones that come up when traders start getting serious about risk management.
What Is The Most Important Rule In Risk Management Trading?
If you only remember one thing, make it this: never risk more than 1-2% of your trading capital on a single trade.
This isn’t just friendly advice; it’s the bedrock survival rule of professional trading. It’s what keeps you in the game.
Sticking to this rule makes it mathematically difficult for a string of losses — which will happen — to blow up your account. More than that, it builds the discipline needed to avoid those gut-wrenching, emotional decisions that can end a trading career before it even starts.
How Do I Determine The Best Place For My Stop Loss?
A good stop-loss isn’t just a random price point. It’s the specific level where your original trade idea is officially proven wrong. You want your analysis, not your fear, to decide where it goes.
Here are a couple of popular, logic-based methods:
- Support and Resistance: For a long (buy) trade, set your stop just below a solid support level. For a short (sell) trade, place it just above a key resistance level.
- Volatility Indicators: Tools like the Average True Range (ATR) can help you set a stop that’s outside the market’s typical daily “noise,” preventing you from getting shaken out of a good trade too early.
The biggest mistake is placing stops too close to your entry. The market needs room to breathe, and a tight stop often gets triggered by normal price wiggles, not a real trend change.
Think of it this way: a well-placed stop-loss is your answer to the question, “At what price is my reason for this trade no longer valid?”
Do I Need A High Win Rate To Be Profitable?
Absolutely not. This is one of the biggest myths in trading, and believing it can be incredibly costly. Profitability isn’t about how often you win; it’s about how much you make when you win versus how much you lose when you’re wrong.
A trader can be consistently profitable winning only 40% of their trades if their winning trades are significantly larger than their losing ones.
Let’s look at two traders:
- Trader A has a 70% win rate. They make $50 on winners but lose $150 on losers. After 10 trades, they’re actually down $100 (7 wins x $50 = +$350; 3 losses x $150 = -$450).
- Trader B only wins 40% of the time. But they make $300 on winners and lose just $100 on losers. After 10 trades, they’re up $600 (4 wins x $300 = +$1200; 6 losses x $100 = -$600).
Forget about being right all the time. Focus on making sure your wins are big and your losses are small.
Ready to stop guessing and start analyzing? TradeReview is the free, powerful trading journal built to help you master your risk management. Log your trades, track your performance with detailed analytics, and identify the emotional patterns holding you back. Get the data-driven insights you need to trade smarter by visiting https://tradereview.app today.


