Weekly options offer a thrilling pace, promising quicker potential outcomes compared to their monthly counterparts. But this speed can be a double-edged sword. We understand the struggle. Many traders, drawn by the allure of rapid gains, jump in without a plan, only to face confusion, stress, and unnecessary losses from the rapid time decay and volatile price swings. This isn’t about finding a magic formula for overnight riches, because such a thing doesn’t exist in trading.
Instead, this guide is built on a foundation of empathy for the trader’s journey. Navigating volatile markets is tough, and the discipline required to succeed is immense. This article is your roadmap, designed to equip you with a diverse set of weekly options trading strategies that can be applied to different market conditions. We will move beyond abstract theory and provide actionable frameworks and practical examples you can start testing.
Here, we’ll break down nine distinct strategies, not as get-rich-quick schemes, but as sophisticated tools for your trading toolbox. Each one comes with practical implementation details, clear risk considerations, and an emphasis on the long-term thinking required to build a sustainable trading career. Whether you are looking to generate income, hedge a position, or speculate on short-term price movements, the goal is to help you approach these powerful instruments with the respect, discipline, and strategic mindset they demand. Let’s explore how to navigate this fast-paced environment with a plan.
1. Iron Condor Strategy
The Iron Condor is a premier choice for traders anticipating low volatility in an underlying asset. This non-directional, income-focused approach is one of the most popular weekly options trading strategies because it can profit when a stock or ETF price remains within a defined range. It is constructed by simultaneously selling an out-of-the-money (OTM) call credit spread and an OTM put credit spread on the same underlying, with the same weekly expiration date.
Your goal is for the underlying asset’s price to stay between the strike prices of the short call and short put, allowing both spreads to expire worthless. The maximum potential profit is the net premium you collect when opening the position. The maximum risk is limited to the difference between the strikes in either spread, minus the premium received. This is a defined-risk strategy.
When to Use an Iron Condor
This strategy excels in a neutral, range-bound market. It is particularly effective on liquid index ETFs like SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY) or Invesco QQQ Trust (QQQ) during periods of sideways consolidation. For example, if SPY is trading at $540 and you expect it to stay between $530 and $550 for the week, you could sell a 550/555 call spread and a 530/525 put spread. Traders often deploy this strategy when implied volatility (IV) is high, as this inflates the premiums you can collect, widening your break-even points and increasing your potential profit buffer.
Key Insight: The Iron Condor is a bet on price stability and decaying volatility. You are essentially selling time and probability to other market participants. Success hinges on selecting a realistic trading range for the week.
This infographic summarizes the core mechanics of the Iron Condor strategy.
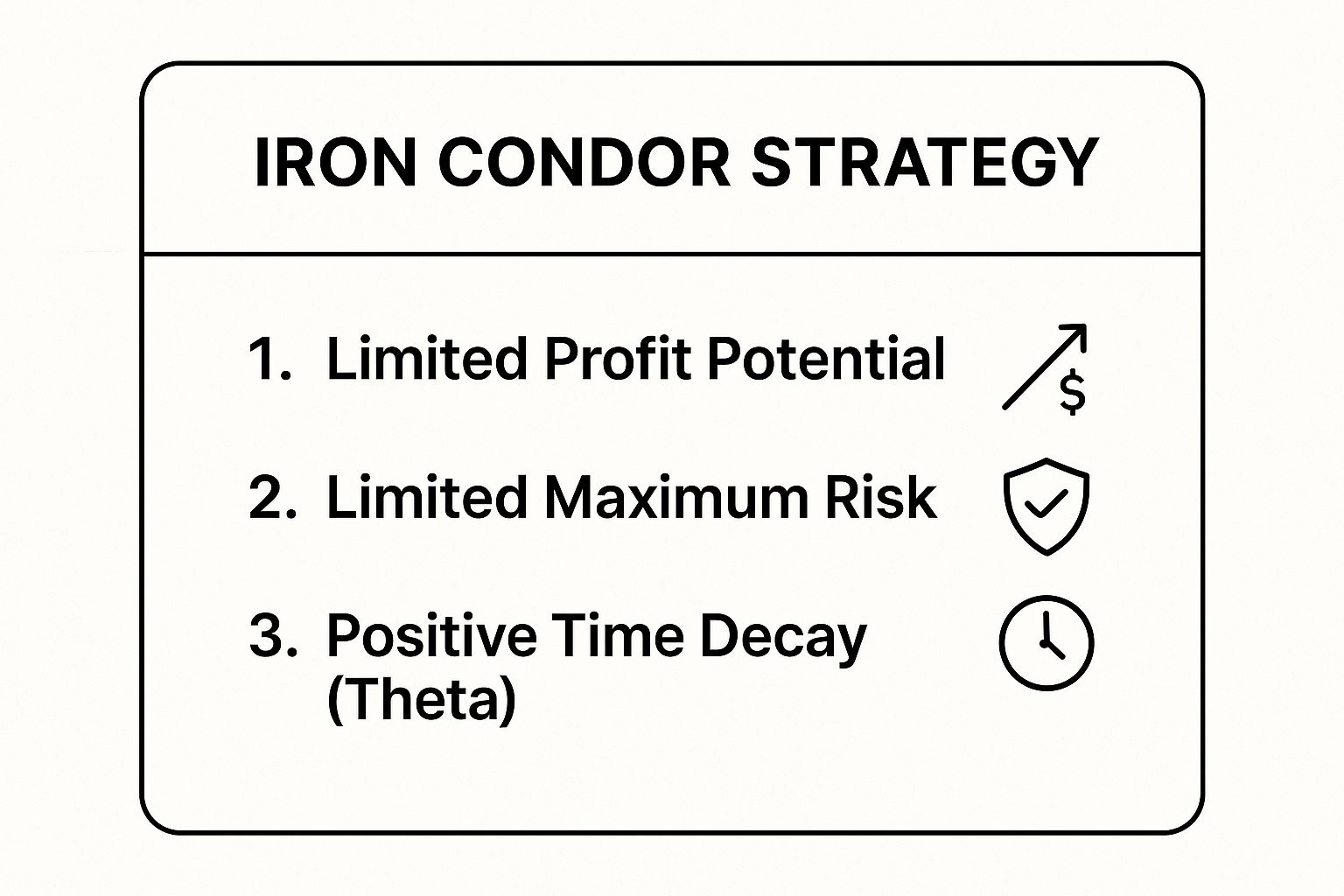
As the visualization highlights, the strategy’s defined risk and profit potential make it a structured way to capitalize on theta decay (time decay) without needing to predict the market’s direction perfectly.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
Discipline is crucial for managing this strategy. Many traders find success by proactively managing the position rather than simply letting the options expire.
- Profit Target: Have a plan. Consider closing the position early once you’ve captured 25-50% of the maximum potential profit. This reduces your exposure to late-week price swings that could turn a winner into a loser.
- Strike Selection: Choose short strikes with a low probability of being touched. A common approach is to select strikes around a 0.20-0.30 delta (delta represents the option’s sensitivity to a $1 change in the underlying stock price). This increases your statistical odds of success.
- Expiration Management: Be cautious holding the position into the last 2-3 days before expiration. This is when gamma risk (the rate of change of delta) increases dramatically, meaning small price moves can have a big impact on your position’s value.
- Liquidity is Key: Only use this strategy on stocks or ETFs with high trading volume and tight bid-ask spreads to ensure you can enter and exit your position at a fair price without significant slippage.
2. Credit Spreads (Bull Put/Bear Call)
Credit spreads are foundational weekly options trading strategies that allow you to generate income by taking a directional view, whether bullish or bearish, with clearly defined risk. This strategy involves selling a higher-premium option and buying a lower-premium option of the same type (both calls or both puts) with the same expiration. The goal is for the underlying asset’s price to stay on one side of your short strike, allowing both options to expire worthless.
There are two primary types: the Bull Put Spread (selling an OTM put and buying a further OTM put) for a neutral-to-bullish outlook, and the Bear Call Spread (selling an OTM call and buying a further OTM call) for a neutral-to-bearish outlook. In both cases, your maximum profit is the net credit received upfront, and your maximum risk is the difference between the strikes minus that credit.
When to Use a Credit Spread
These strategies are ideal when you have a directional bias but want to profit from time decay (theta) while limiting potential losses. They work best on liquid stocks and ETFs where you can identify clear support or resistance levels. For instance, if Tesla (TSLA) is trading at $185 and you believe it will stay above a support level of $180 for the week, you could implement a bull put spread by selling the $180 put and buying the $175 put. This allows you to profit even if TSLA moves sideways or even slightly down, as long as it closes above $180 at expiration.
Key Insight: Credit spreads offer a high probability of success by allowing you to be “wrong” on direction to a degree and still profit. You are paid to be right about where the stock price won’t go.
Success with this strategy hinges on selecting appropriate strike prices based on technical analysis and probability, creating a buffer for minor price fluctuations against your position. You can explore a variety of scenarios with these bull put spread examples to better understand their application.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
Discipline in trade management is what separates consistently profitable spread traders from the rest. A systematic, rule-based approach is essential.
- Profit Target: Don’t be greedy. Systematically close your positions when you achieve 25-50% of the maximum potential profit. Waiting for 100% dramatically increases your risk for a small additional reward.
- Strike Selection: Target short strikes with a 70-80% probability of expiring out-of-the-money (OTM). This typically corresponds to a delta between 0.20 and 0.30.
- Avoid Event Risk: Be cautious placing trades right before earnings reports or other major news events unless you are specifically trading the expected volatility contraction. Unexpected news can cause sharp price moves.
- Use Technical Analysis: Identify key support and resistance levels on a chart to inform your strike selection. Selling puts above support and calls below resistance can improve your odds.
3. 0DTE (Zero Days to Expiration) Trading
Zero Days to Expiration (0DTE) trading is an ultra-short-term, high-risk, high-reward approach where traders buy and sell options on the day they expire. This strategy seeks to profit from intraday price movements, capitalizing on the extremely rapid time decay (theta) that occurs in the final hours of an option’s life. It is one of the most dynamic weekly options trading strategies, often executed on highly liquid indices like the SPX, SPY, and QQQ.
Unlike longer-term strategies, the goal with 0DTE is not to hold for days but for minutes or hours. Traders either make directional bets, buying calls or puts to capture a sharp intraday trend, or they sell premium with strategies like iron condors, betting the underlying will stay within a tight range for just a few hours. Success demands precision, discipline, and constant market monitoring. Many traders struggle with the emotional discipline required.
When to Use 0DTE Trading
This strategy is best suited for experienced day traders who can dedicate their full attention to the market during trading hours. It is most effective on days with clear catalysts, such as major economic data releases (e.g., CPI, FOMC announcements) or significant market-moving news that can create predictable, short-term trends. For example, a trader might buy SPY 0DTE calls immediately following a better-than-expected jobs report, aiming to ride the initial bullish momentum for a quick profit before sentiment shifts.
Key Insight: 0DTE trading is a direct play on intraday gamma and theta. Gamma risk is at its absolute peak, meaning small price moves in the underlying can cause explosive changes in the option’s price. You are trading a rapidly depreciating asset, which requires flawless timing and emotional control.
This infographic summarizes the high-stakes nature of 0DTE trading.

As the visualization implies, the accelerated profit potential is matched by the risk of a total loss if the trade moves against you, making risk management paramount.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
Discipline in 0DTE trading is not just a suggestion; it’s a requirement for survival. The speed of these trades leaves no room for emotional decisions or hesitation.
- Risk Management: This is non-negotiable. Never risk more than a small fraction (e.g., 0.5% to 1%) of your account on a single trade. The potential for a 100% loss is very real.
- Precise Timing: Use technical analysis on short-term charts (1-minute, 5-minute) to identify precise entry and exit points. Avoid trading in the first and last 30 minutes of the session, as volatility can be erratic and unpredictable.
- Predetermined Exits: Always enter a trade with a clear profit target and a hard stop-loss. Given the speed, consider using bracket orders to automate your exits and remove emotion from the decision.
- Focus on Liquidity: Stick exclusively to highly liquid index options like SPX, SPY, and QQQ. Their tight bid-ask spreads are essential for minimizing slippage on fast-moving trades.
4. Straddle and Strangle Strategies
The Straddle and Strangle are classic volatility strategies designed to profit from significant price movement, regardless of direction. These are powerful weekly options trading strategies for traders who anticipate a sharp move but are uncertain of the catalyst’s outcome. A long straddle involves simultaneously buying a call and a put at the same strike price, while a long strangle involves buying an out-of-the-money (OTM) call and an OTM put.
Your goal is for the underlying asset to make a move substantial enough to overcome the total premium paid for both options. Conversely, short straddles and strangles involve selling both options to collect premium, profiting if the underlying stays within a defined range. The long versions are long volatility plays, while the short versions are short volatility plays.
When to Use a Straddle or Strangle
These strategies are ideal for binary events where a large price swing is expected, such as earnings announcements, major economic data releases, or FDA rulings. For example, if NVIDIA (NVDA) is set to report earnings and you expect a massive reaction but are unsure if it will be positive or negative, a long straddle or strangle allows you to capitalize on the resulting volatility. Short versions are best used when implied volatility (IV) is exceptionally high and expected to contract, and you anticipate the underlying will remain relatively stable.
Key Insight: A long straddle or strangle is a direct bet on future volatility being greater than what the market is currently pricing in. Success depends on the magnitude of the price move, not the direction.
The defined-risk nature of the long straddle and strangle makes them popular for speculative plays around news events, while the short versions are favored by experienced traders for income generation in high-IV environments.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
Discipline in managing these positions is vital, as time decay (theta) can rapidly erode the value of long positions, and gamma risk can expose short positions to unlimited losses if unmanaged.
- Event-Driven Trades: For long positions, consider entering the trade a few days before a high-impact event and plan to exit shortly after the news is released. This helps avoid post-event “volatility crush” (a rapid decrease in implied volatility) which can hurt your position’s value.
- Implied Volatility is Crucial: For short positions, sell straddles and strangles when implied volatility rank (IVR) is high (e.g., above 50). This inflates the premium you collect and provides a wider margin for error.
- Risk Management: Never use a naked short straddle or strangle unless you are an advanced trader with a significant risk tolerance. Consider a defined-risk alternative like an Iron Condor or Iron Butterfly instead to cap potential losses.
- Profit Taking: For long positions, exit once the underlying makes its move. Don’t wait for more, as time decay is constantly working against you. For short positions, have a plan to close for 25-50% of the maximum profit.
5. Butterfly Spreads
The Butterfly Spread is a precise, neutral strategy designed for traders who believe an underlying asset’s price will remain exceptionally stable. This is one of the more advanced weekly options trading strategies, offering a high reward-to-risk ratio but requiring the underlying to “pin” a specific price at expiration. It is constructed using three different strike prices, typically by buying one in-the-money option, selling two at-the-money options, and buying one out-of-the-money option.
Your goal is for the underlying asset’s price to be exactly at the middle (short) strike price at expiration. This is where you achieve maximum profit. The strategy is defined-risk, with the maximum loss limited to the net debit paid to enter the trade. This combination of low cost and high potential payout makes it an attractive, albeit lower-probability, approach.
When to Use a Butterfly Spread
This strategy thrives in a market with extremely low expected movement, especially when you can pinpoint a likely closing price for the week. It is often used on high-volume ETFs like the SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY) during periods of tight consolidation. For example, if SPY is trading at $540 and you believe it will close the week at that exact price, you could place a long 535/540/545 call butterfly.
Key Insight: A long Butterfly Spread is a bet on ultimate price precision and time decay. You are targeting a very narrow profit window, and your greatest enemy is a significant price move in either direction.
This strategy requires patience and an understanding that achieving maximum profit is rare; the real art is in managing the trade for a smaller, more probable gain.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
Discipline in managing a Butterfly is paramount due to its sensitivity to price as expiration nears. Proactive management is often more effective than holding until the final moments.
- Profit Target: It’s wise to set a realistic goal. Aim to close the position for a 25-50% return on your initial investment. Waiting for the maximum payout is statistically unlikely and exposes you to significant gamma risk.
- Strike Selection: Center your short strikes as close to the current price of the underlying as possible, or at a key support/resistance level where you anticipate the stock will gravitate.
- Volatility: Consider entering Butterfly Spreads when implied volatility (IV) is relatively high. This can allow you to construct the spread for a lower net debit, improving your risk-reward profile.
- Expiration Management: Be prepared to close the position before the final trading day. As expiration approaches, the position’s value can swing wildly with even small price changes, making it difficult to manage.
6. Gamma Scalping
Gamma Scalping is an advanced, market-neutral strategy favored by professional traders who aim to profit from an asset’s volatility rather than its price direction. It involves creating a long gamma, delta-neutral position (typically by buying a straddle or strangle) and then actively trading the underlying stock to keep the position’s delta close to zero. This dynamic hedging is one of the more complex weekly options trading strategies, turning realized volatility into tangible profit.
The core idea is to buy options when you believe the underlying asset’s actual (realized) volatility will be greater than its implied volatility (IV). As the stock price moves, your position’s delta changes due to gamma. You then “scalp” shares of the underlying — buying when the price drops and selling when it rises — to re-neutralize your delta and lock in small profits from these price swings.
When to Use Gamma Scalping
This strategy is best deployed when you anticipate significant price movement in an underlying asset but are unsure of the direction. It is particularly effective on highly liquid ETFs like SPY or individual stocks with upcoming catalysts, such as earnings announcements, where a large price swing is likely. If you believe the market is underpricing the potential for sharp, back-and-forth movement, a gamma scalp allows you to monetize that volatility.
Key Insight: Gamma Scalping is a direct bet on volatility itself. You profit if the stock moves more than the options market has priced in, regardless of the final direction. Success depends on active, disciplined hedging.
For traders looking to understand the mechanics of frequent, small-profit trades, it’s helpful to explore the core principles of scalping. To delve deeper, you can learn more about scalping on tradereview.app. This foundational knowledge is crucial for executing the hedging component of a gamma scalp effectively.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
Discipline and precision are paramount, as this is an active management strategy, not a passive one. Poor execution or high transaction costs can quickly erode potential profits.
- Liquidity is Non-Negotiable: Only attempt this on underlyings with massive volume and extremely tight bid-ask spreads to minimize slippage on your frequent stock trades.
- Monitor Volatility Spreads: The trade is only profitable if realized volatility exceeds the implied volatility you paid for. Track this relationship closely.
- Commission Awareness: Your profitability is directly impacted by transaction costs. Ensure your broker’s commission structure is favorable for high-frequency stock trading.
- Start Small: Practice makes perfect. Begin with a single options contract and a small number of shares to understand the mechanics and management intensity before scaling up your position size.
7. Covered Call Writing
The Covered Call is a foundational strategy for investors looking to generate income from their existing stock holdings. It is one of the most widely used weekly options trading strategies because it allows you to earn a premium by selling call options against shares you already own. This strategy is ideal in a neutral to slightly bullish market where you do not expect a dramatic price increase in the near term.
The mechanics are straightforward: for every 100 shares of a stock you own, you sell one call option contract. The premium you receive provides an immediate cash inflow, effectively lowering your cost basis or creating a new income stream. Your goal is for the stock price to stay below the call’s strike price, allowing the option to expire worthless so you can keep the premium and your shares.
When to Use a Covered Call
This strategy excels when you want to enhance the yield on a long-term stock position or believe a stock will trade sideways or appreciate modestly. For example, if you own 100 shares of Apple (AAPL) trading at $210 and you don’t expect it to rally past $215 in the next week, you could sell a weekly call with a $215 strike price. The premium collected provides a small buffer against a price drop and adds to your overall return if the stock remains below $215. It’s also frequently used on dividend-paying stocks to compound income.
Key Insight: A Covered Call is not a bet on massive upside; it’s a trade-off. You are agreeing to cap your potential stock gains for the week in exchange for receiving a guaranteed premium today.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
Discipline in strike selection and position management is vital for long-term success with covered calls. The goal is to consistently generate income without having your shares called away unexpectedly at a disadvantageous price.
- Strike Selection: Sell calls with a strike price above a known technical resistance level. Choosing a strike with a delta (a measure of directional exposure) between 0.20 and 0.40 often provides a good balance between premium received and the probability of the option expiring out-of-the-money.
- Willingness to Sell: Only write covered calls on stocks you are genuinely willing to sell at the strike price. If the stock soars past your strike, you will miss out on those additional gains.
- Managing a Challenged Position: If the stock price rises and challenges your short call strike, you can often “roll” the position. This involves buying back your current short call and selling a new one with a later expiration date and a higher strike price, often for a net credit.
- Avoid Earnings: Be very cautious about selling calls right before an earnings report. A surprisingly positive announcement could cause the stock to gap up significantly, forcing the sale of your shares and capping your upside.
8. Momentum Breakout Options
The Momentum Breakout strategy is a directional approach designed for traders who believe an asset is about to make a significant move. This technique involves buying call or put options when a stock breaks through a critical technical level, like resistance or support, ideally on high volume. It is one of the more aggressive weekly options trading strategies, using options to leverage a strong anticipated continuation of the price move with clearly defined risk.
Your goal is to capitalize on a sudden surge in price driven by a shift in market sentiment. By purchasing a call option on a breakout above resistance or a put option on a breakdown below support, you position yourself to profit from the expected follow-through. The maximum risk is limited to the premium paid for the option, while the profit potential is theoretically unlimited, though realistically tied to the strength and duration of the breakout.
When to Use Momentum Breakout Options
This strategy thrives in trending markets where a clear catalyst or technical pattern triggers a strong directional move. It is best applied to stocks or ETFs that have been consolidating in a range and are now showing signs of a decisive break. For example, if QQQ has been trading below a key resistance level of $450 and suddenly pushes above it with a surge in trading volume, a trader might buy a weekly $455 call option to profit from the expected upward momentum.
Key Insight: This strategy is a bet on trend continuation, not just a price change. Success depends on identifying genuine breakouts with conviction, often confirmed by indicators like volume, and acting swiftly to capture the initial thrust of the new trend.
This method allows you to participate in powerful moves without the capital commitment of buying the underlying shares. You can learn more about the core principles by reading up on what momentum trading is.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
Discipline is paramount to avoid chasing “false breakouts,” which are common market traps that can lead to quick losses. A systematic approach helps filter out low-probability trades and manage risk effectively.
- Confirm with Volume: A true breakout should be accompanied by a significant increase in trading volume. This confirmation suggests institutional participation and conviction behind the move.
- Set Clear Profit Targets: Don’t get greedy. Momentum can fade quickly. Aim to take profits when you’ve achieved a substantial gain, such as 50-100% of the premium paid.
- Use Technical Stop-Losses: Although your risk is defined by the premium, have a mental or actual stop-loss based on the underlying’s price. If the stock falls back below the breakout level, it may be time to cut the position to preserve remaining premium.
- Time Value is Your Friend: Avoid buying options that are too close to expiration. Choose weekly options with enough time (at least 2-3 weeks out, if possible) to allow the momentum move to fully develop without rapid time decay (theta) eroding your position’s value.
9. Volatility Crush Plays
Volatility Crush Plays are designed to profit from the rapid decrease in an option’s implied volatility (IV) following a major, scheduled event. This is one of the more event-driven weekly options trading strategies, capitalizing on the predictable inflation and subsequent collapse of option premiums around uncertain outcomes like earnings reports, FDA announcements, or Federal Reserve meetings. The core idea is to sell options or spreads when IV is high just before the event, then buy them back for a lower price after the news is released and uncertainty vanishes.
The strategy’s success depends less on the stock’s price direction and more on the volatility returning to normal levels. When an event’s outcome is unknown, the demand for options (as a form of insurance or speculation) skyrockets, pumping up their prices. Once the news is public, this uncertainty premium evaporates, causing a “volatility crush,” which is what the trader aims to capture as profit.

When to Use a Volatility Crush Play
This strategy is specifically for trading around known, market-moving events where IV is historically elevated. It is a bet against the magnitude of the expected price move. For instance, if traders expect a stock like Netflix (NFLX) to move +/- 10% after earnings, but you believe the actual move will be smaller, you could sell a short strangle or an iron condor. The goal is for the post-event price move to be less than what the inflated option premiums had priced in, allowing you to profit from the IV collapse.
Key Insight: A Volatility Crush Play is a bet that the market’s fear (reflected in high IV) is greater than the impending reality. You are essentially selling insurance to others when the perceived risk is at its peak.
This advanced strategy is not for the faint of heart. The underlying stock can still make an unexpectedly large move, and selling options carries significant risk if not properly managed.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
Discipline and a deep understanding of volatility are crucial. The goal is to survive the price move and capture the IV drop.
- Use Defined-Risk Strategies: Instead of selling naked options (which have undefined risk), consider using defined-risk structures like iron condors or credit spreads. This caps your maximum potential loss if the stock makes an outsized move against your position.
- Analyze Historical Volatility: Before entering a trade, check how the stock has behaved after past earnings reports. Did IV always crush? Did the stock often move more or less than expected? This data provides a valuable edge.
- Close Promptly: The volatility crush often happens within minutes or hours of the event. Plan to close your position quickly after the news is out to lock in profits from the IV drop and avoid further directional risk.
- Check IV Rank/Percentile: Only consider these plays when the underlying’s implied volatility rank (IVR) or percentile is high (e.g., above 50). This confirms that option premiums are genuinely expensive and worth selling.
Weekly Options Strategies Comparison Table
| Strategy | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iron Condor Strategy | High – Four-leg options strategy, complex to manage | Moderate – Margin and commissions | Limited profit, limited risk, consistent income in range-bound markets | Neutral market, low volatility periods | Limited max loss, profits from time decay, high success in sideways markets |
| Credit Spreads (Bull Put/Bear Call) | Moderate – Two-leg options, directional bias | Low to Moderate – Lower capital needed | Limited profit, immediate credit, high probability success | Directional bullish/bearish setups | Immediate income, time decay benefit, flexible strikes |
| 0DTE Trading | Very High – Same-day expiration, active monitoring | High – Requires focus and quick action | Rapid profit potential, no overnight risk, very high risk | Intraday trades, day trading, volatility plays | Quick gains, no overnight exposure, high leverage |
| Straddle and Strangle Strategies | High – Need volatility awareness, two options | Moderate – Double commission costs | Profit from big moves (long) or stability/time decay (short) | Volatility plays, event-driven trades | Direction-neutral, profits from volatility, multiple scenarios |
| Butterfly Spreads | High – Three-strike, precise price prediction needed | Low to Moderate – Lower cost than straddles | Limited risk and reward, profits near middle strike | Low volatility, precise price targets | Limited max loss, high risk-adjusted profit potential |
| Gamma Scalping | Very High – Dynamic hedging, active management | High – High transaction costs | Consistent returns from volatility without directional bias | Market-neutral volatility trading | Profits from gamma, scalable, less market direction risk |
| Covered Call Writing | Low – Requires stock ownership, simple to execute | Low to Moderate – Requires stock capital | Income generation, limited upside, cost reduction | Income-focused, sideways/slightly bullish markets | Immediate income, lowers position cost, conservative |
| Momentum Breakout Options | Moderate – Directional, technical analysis based | Moderate – Needs good timing | High profit potential during strong moves | Breakouts with volume, trending markets | High profits on trends, defined risk, flexible sizing |
| Volatility Crush Plays | High – Event-driven, precise timing needed | Moderate – Risk management crucial | Profits from volatility drop after events | Earnings, FDA approvals, economic events | High probability, consistent returns, event-focused |
From Strategy to Success: The Discipline of Execution
We have navigated a diverse landscape of powerful weekly options trading strategies. From the calculated risk management of the Iron Condor to the aggressive precision of 0DTE plays, each strategy offers a unique tool for your trading arsenal. You have seen how to generate income with Credit Spreads, capitalize on explosive moves with Straddles, and harness momentum with Breakout Options.
The common thread weaving through all these approaches is not a secret formula for easy profits, but the non-negotiable demand for discipline, risk management, and continuous learning. Knowing the mechanics of a Bull Put Spread is one thing; executing it consistently, managing it under pressure, and learning from the inevitable losses is what separates aspiring traders from profitable ones. The market is a relentless teacher, and its lessons are often expensive. We’ve all been there.
Bridging the Gap Between Knowledge and Profitability
The true challenge begins now. The journey from understanding these strategies to achieving consistent success is paved with meticulous execution and honest self-assessment. It is easy to get caught up in the emotional rollercoaster of a winning or losing streak, but feelings are poor indicators of performance. Data, on the other hand, is brutally honest and endlessly insightful.
This is where the real work of a trader happens, away from the charts and the thrill of the trade. It happens in the quiet moments of review, where you deconstruct your decisions and identify what works for you.
Key Takeaways for Sustainable Growth:
- Strategy Is Not a Silver Bullet: No single strategy works in all market conditions. Your success depends on your ability to select the right tool for the current environment — a high-implied-volatility environment might favor an Iron Condor, while a trending market might call for a momentum play.
- Risk Management Is Paramount: Your primary job is not to be right on every trade but to ensure that your losses are managed so you can stay in the game long enough to let your winning strategies work. Position sizing and stop-loss discipline are your most critical skills.
- Performance Review Is Non-Negotiable: The most significant growth comes from analyzing your own trading data. Without a structured review process, you are doomed to repeat the same mistakes. You must move beyond gut feelings and analyze the hard numbers to build long-term success.
Your Path Forward: The Power of a Trading Journal
To truly master these weekly options trading strategies, you must treat your trading like a business. The most effective way to do this is by maintaining a detailed trading journal. A journal transforms every trade, win or lose, into a valuable data point. It is your personal performance database, revealing patterns in your behavior and strategy that you would otherwise completely miss.
Instead of guessing why you are struggling, a journal can provide concrete answers.
- Are your losses on Bear Call Spreads consistently larger than your wins?
- Do you tend to close your profitable Straddles too early before a big move?
- Is your win rate on 0DTE trades high, but a few large losses wipe out all the gains?
These are the questions that pave the road to profitability. Answering them requires moving beyond a simple spreadsheet and embracing tools designed for deep analysis. By logging your rationale, the strategy used, entry/exit points, and market context for every trade, you create a feedback loop that accelerates your learning curve exponentially. Don’t just trade these strategies; test them, track them, and refine them based on your own results. True mastery comes not from finding the perfect strategy, but from perfecting your personal process of execution and review.
Ready to turn theory into a data-driven process? Start tracking your weekly options trading strategies with TradeReview to get an unbiased, analytical view of your performance and uncover your true edge. Sign up for free and begin your journey toward disciplined trading today at TradeReview.


