Welcome to the world of trading, a landscape filled with immense opportunity but also significant challenges. Many enter the market drawn by the allure of quick profits, only to face the harsh realities of emotional decision-making and unexpected losses. We understand the struggle because we’ve seen it time and again. This isn’t another guide promising ‘guaranteed profits’ or a secret formula. Instead, this is an empathetic, practical collection of hard-won wisdom, actionable tips for traders designed to build discipline, foster long-term thinking, and equip you with a professional mindset.
Our goal is to move beyond generic advice. We will provide concrete examples and specific strategies that you can implement today to start building a sustainable trading career. Whether you are an experienced day trader looking to refine your approach or an investor interested in tracking stocks and options more effectively, these principles are foundational. They address the core pillars of successful trading: planning, risk management, psychology, and continuous improvement.
In this comprehensive roundup, we will explore eight essential concepts. You will learn how to develop a robust trading plan, master position sizing, manage the psychological pressures of the market, and leverage tools like a trading journal to analyze your performance. Each tip is presented with actionable steps and real-world scenarios to help you turn theory into practice. These eight principles will serve as your roadmap to navigating the markets with greater confidence and control, transforming your trading from a game of chance into a structured business. Let’s begin.
1. Develop and Stick to a Trading Plan
Failing to plan is planning to fail, a cliché that holds profound truth in the world of trading. A trading plan is your personal business plan; it is a structured, written document that outlines every aspect of your trading activity. This isn’t just a vague set of goals; it’s a concrete framework governing your decisions, designed to eliminate impulsive, emotion-driven actions that often lead to significant losses. Think of it as the constitution for your trading business, providing the rules of engagement for any market scenario.
This comprehensive roadmap dictates your trading objectives, risk tolerance, and the specific strategies you will employ. It covers everything from the markets you’ll trade and the hours you’ll be active to the precise criteria for entering and exiting a position. By defining these parameters before you enter the market, you create a system of accountability that fosters discipline and consistency, two of the most critical traits for long-term success.
Why a Trading Plan is Non-Negotiable
A well-defined plan acts as your primary defense against the psychological pressures of trading, such as fear and greed. When a trade moves against you, your plan tells you exactly where your stop-loss is, preventing a small, manageable loss from becoming a catastrophic one. For instance, imagine a trade on Apple (AAPL) starts to drop. Without a plan, you might panic and sell, or worse, hold on hoping it recovers. With a plan, your pre-defined exit at a specific support level or moving average cross takes the emotion out of the decision. This systematic, repeatable process is what separates professionals from amateurs.
This bar chart highlights the core components, benefits, and potential drawbacks of implementing a trading plan.
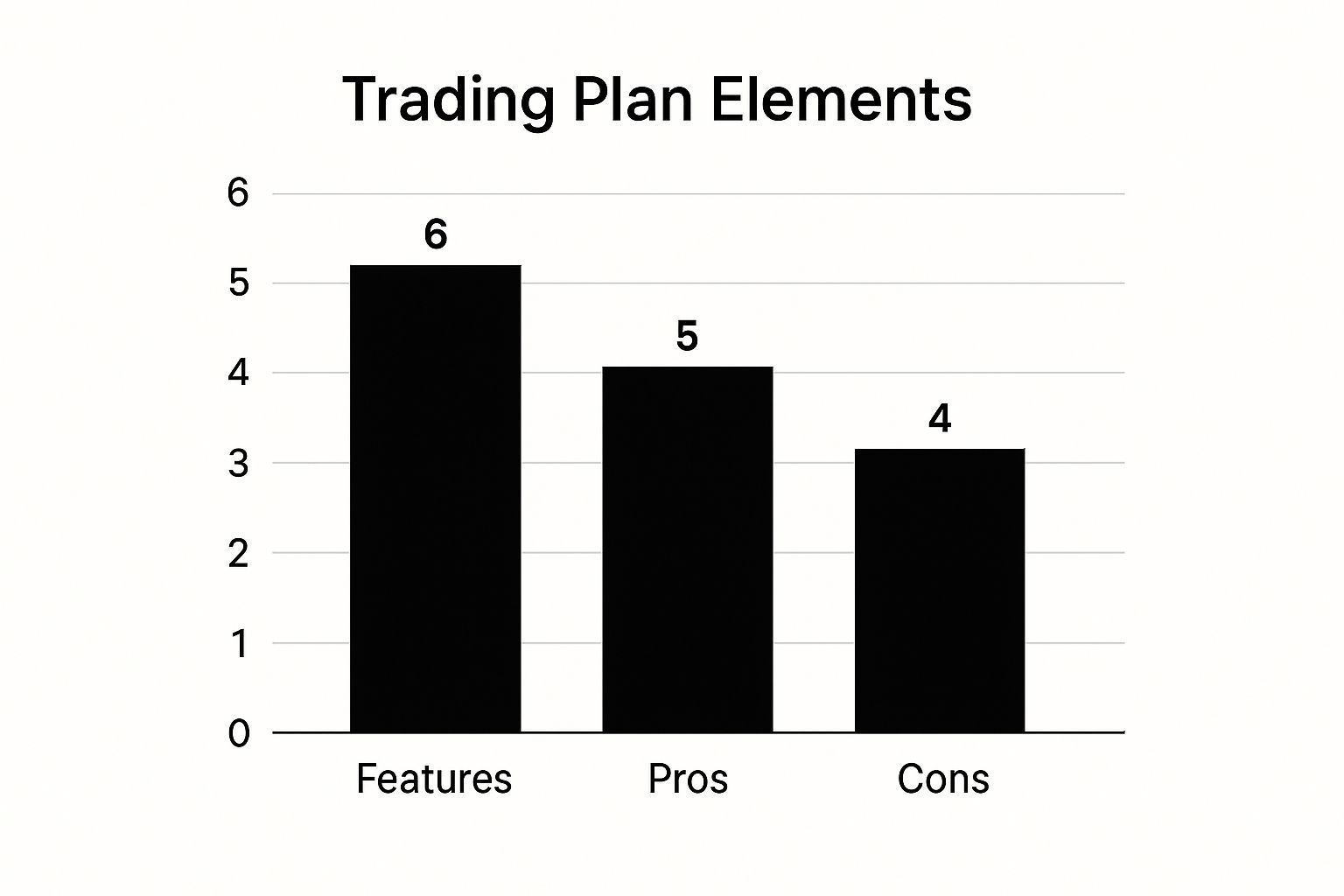
The chart visually demonstrates that the essential features and direct benefits of a trading plan significantly outnumber the perceived drawbacks, emphasizing its foundational importance.
How to Create and Implement Your Plan
Building your plan doesn’t have to be overly complex. Start simple and refine it as you gain experience.
- Define Your “Why”: What are your financial goals? Are you aiming for supplemental income or long-term wealth creation? Be specific. Example: “My goal is to generate an average of $500 per month to supplement my income.”
- Establish Entry/Exit Rules: What technical or fundamental signals must be present for you to enter a trade? What signals will tell you it’s time to take profit or cut a loss? Example: “I will enter a long trade on SPY only when the 50-day moving average crosses above the 200-day moving average and the RSI is below 70.”
- Set Risk Parameters: Determine your risk-per-trade (e.g., never risk more than 1% of your account on a single trade) and your maximum drawdown (the point at which you stop trading for the day or week).
- Write It Down: Physically write or type out your plan. Review it before every trading session to reinforce your rules.
- Test and Refine: Use paper trading or a backtesting platform to validate your strategy before committing real capital. Regularly review your performance (quarterly is a good starting point) and update your plan based on hard data from your trading journal, not on emotions.
2. Master Risk Management and Position Sizing
While a profitable strategy is essential, it’s a robust risk management framework that truly separates professional traders from amateurs. Risk management is the art of capital preservation; it ensures that no single trade or string of losses can wipe out your account. It’s not about avoiding losses, which are an inevitable part of trading, but about controlling them so you can stay in the game long enough for your edge to play out.
Position sizing is the practical application of risk management, dictating exactly how much capital you allocate to a single trade based on your predefined risk tolerance. This methodical approach to capital allocation is arguably the most critical of all tips for traders, as it directly controls your potential drawdowns and emotional stability. It’s the defensive play that enables your offensive strategy to succeed over the long term.

Why Risk Management is Your Primary Job
Your first job as a trader is not to make money, but to protect the capital you have. Without capital, you cannot trade. We’ve all felt the sting of a big loss and the urge to “make it back” on the next trade. This is called “revenge trading,” and it’s a primary account killer. A sound risk plan is your objective guide in the heat of the moment, preventing one bad decision from turning into a devastating series of them. Proper risk management ensures your long-term survival, which is the prerequisite for long-term profitability.
This video provides a practical overview of how to apply risk management principles to your trading.
How to Implement and Master Risk Control
Effective risk management is systematic and calculated, not improvised. Integrate these practices into your trading routine.
- Define Your Risk-Per-Trade: The 1% rule is a great starting point. This means you never risk more than 1% of your total account equity on a single trade. For a $25,000 account, your maximum loss on any given trade would be $250. This creates sustainability.
- Calculate Position Size Before Entry: Your position size should be determined by your stop-loss distance, not the other way around. Practical example: If you want to buy a stock at $100 with a stop-loss at $98, your risk per share is $2. With a $25,000 account and a 1% risk rule, you can risk $250. Your position size is $250 / $2 = 125 shares.
- Use Stop-Loss Orders Religiously: A stop-loss order is a non-negotiable instruction to exit a trade at a specific price, guaranteeing your loss does not exceed your predefined risk.
- Aim for Asymmetrical Risk-Reward: Only take trades where the potential profit is at least twice the potential loss (a 1:2 risk-reward ratio or better). This ensures that your winning trades will more than cover your losing ones over time.
- Track Your Maximum Drawdown: Monitor the largest peak-to-trough decline in your account value. Keeping this figure below 20% is a common professional benchmark. To dive deeper into a variety of methods, explore these advanced risk management techniques.
3. Control Your Emotions and Trading Psychology
The most sophisticated trading strategy in the world is useless if you lack the mental fortitude to execute it. Trading psychology is the discipline of managing your emotional and mental state to make objective, logical decisions. The market is a relentless battlefield of emotions-primarily fear and greed-that can sabotage even the most talented analyst, making emotional control one of the most vital tips for traders to master.

This battle is not fought on the charts but within your own mind. We’ve all been there: a trade goes against you, and fear makes you sell right before it turns around. Or, after a big win, greed makes you take the next, less-than-ideal setup, and you give back all your profits. Mastering your psychology means developing a systematic process that minimizes the impact of these destructive impulses, allowing your well-researched plan to operate as intended.
Why Trading Psychology is a Game-Changer
The history of trading is filled with brilliant minds who failed due to poor emotional control. The market is an expert at exploiting our cognitive biases. For example, ‘confirmation bias’ will make you seek out information that supports your losing trade instead of objectively seeing the reasons to exit. ‘Fear of missing out’ (FOMO) will push you to chase a stock that has already made a huge move. Recognizing these internal struggles is the first step toward building a professional, resilient mindset.
This chart breaks down the common emotional pitfalls traders face, their potential consequences, and effective psychological countermeasures.

The graphic clearly shows how proactive psychological techniques directly address the most common and destructive emotional trading errors, highlighting the importance of mental preparation.
How to Cultivate Emotional Discipline
Developing emotional control is an ongoing practice, not a one-time fix. Here are actionable steps to build your mental edge.
- Journal Your Emotions: Keep a detailed trading journal that logs not just your trades, but your emotional state before, during, and after each one. Were you anxious? Overconfident? This creates self-awareness.
- Implement a “Cool-Down” Period: After a large win or a frustrating loss, step away from the screen for at least 30 minutes. This break prevents “revenge trading” or euphoria-driven mistakes.
- Use Pre-Trade Checklists: Before entering any trade, run through a checklist that confirms the setup meets your plan’s criteria and that you are in a calm, focused state.
- Set Firm Stop-Loss Rules: Define your maximum daily or weekly loss limit. If you hit it, you must stop trading. This rule is non-negotiable and acts as a circuit breaker for emotional spirals.
- Focus on Process, Not Profit: Celebrate perfect execution of your plan, regardless of the trade’s outcome. This shifts your focus from the uncontrollable (market movements) to the controllable (your actions).
4. Start Small and Scale Gradually
One of the most common and costly mistakes new traders make is entering the market with too much size, too soon. The principle of starting small and scaling gradually is a cornerstone of sustainable trading, serving as a form of self-imposed risk management during the critical learning phase. It involves beginning your live trading journey with minimal capital and small position sizes, allowing you to experience the psychological pressures of real money without risking financial ruin. This approach protects your capital while you build invaluable skills and emotional resilience.
Think of it as an apprenticeship. You wouldn’t expect to run a multi-million dollar company on your first day; similarly, you shouldn’t try to manage a large trading account without proven, consistent performance. By starting small, you give yourself the space to make inevitable beginner mistakes when the financial consequences are minor. This builds the proper habits and discipline needed to handle larger sums of money responsibly down the road.
Why a Gradual Approach is Non-Negotiable
Scaling gradually is your defense against the Dunning-Kruger effect, where early, lucky success can create a dangerous overconfidence. It forces you to prove your strategy’s edge over a meaningful period before increasing your exposure. For example, a new trader might have a great first week and, feeling invincible, double their position size. A normal market pullback then results in a devastating loss because they weren’t psychologically prepared for the larger dollar swings. Starting small allows you to adapt to the emotional stress of larger positions incrementally, preventing this kind of shock.
This strategy ensures that your confidence is built on a foundation of tangible results, not on a handful of fortunate trades. It allows you to adapt to the emotional stress of larger positions incrementally, preventing the psychological shock that can come from a significant loss on a position size you are not yet prepared to handle.
How to Create and Implement Your Scaling Plan
A structured scaling plan removes emotion from the decision to increase your risk. It should be based on objective performance metrics.
- Define Your Starting Size: Begin with a position size that feels almost insignificant, perhaps risking just 0.25% of your account per trade instead of the full 1%. For forex traders, this could mean using micro accounts.
- Set Clear Milestones: Establish specific, written criteria for scaling up. For example, you must achieve three consecutive months of profitability before increasing your standard position size by 50%.
- Increase Incrementally: When you meet your milestone, don’t double your size overnight. A controlled increase of 25-50% is more prudent, allowing you to adjust to the new risk level.
- Be Prepared to Scale Down: If your performance falters after increasing your size, it’s a clear signal that you weren’t ready. Immediately scale back to your previous level and re-evaluate. This is a sign of strength, not failure.
- Track Your Emotions: As you scale, use your trading journal to note your emotional state. Are you more anxious? Are you hesitating or making impulsive decisions? This psychological data is as important as your profit and loss.
5. Keep a Detailed Trading Journal
If your trading plan is the constitution for your business, your trading journal is its performance logbook and strategic archive. A trading journal is far more than a simple list of wins and losses; it is a comprehensive record of your trading activity, capturing the “why” and “how” behind every decision. It documents entry and exit points, position sizes, market conditions, your emotional state, and the specific rationale for taking the trade. This transforms trading from a series of isolated bets into a measurable, data-driven skill.
This systematic documentation serves as your personal learning database. By consistently recording and reviewing your actions, you uncover hidden patterns in your behavior, both positive and negative. It forces an objective look at your performance, helping you distinguish between a well-executed trade that lost money and a poorly executed trade that got lucky. This process of self-evaluation is one of the most powerful tips for traders aiming for consistent improvement and professional-level results.
Why a Trading Journal is a Game-Changer
A journal is your primary tool for deliberate practice, turning raw experience into refined expertise. It’s the feedback loop that prevents you from repeating the same mistakes indefinitely. Imagine you keep losing money on Friday afternoons. Without a journal, you might not notice this pattern. With a journal, the data becomes undeniable, allowing you to adjust by either stopping trading early on Fridays or being extra selective with your setups. This is how professionals identify and eliminate their weaknesses.
Trading without a journal is like a scientist conducting experiments without recording the results; progress becomes impossible. It provides the hard data needed to validate your strategies, identify emotional triggers like fear or overconfidence, and hold yourself accountable to your trading plan. For professional firms, journaling isn’t optional; it’s a mandatory component of their trader development programs because they understand it is the foundation of long-term profitability.
How to Create and Implement Your Journal
Your journal can be a simple spreadsheet or utilize specialized software like TraderSync or Edgewonk. The key is consistency and detail.
- Log Trades in Real-Time: Record data immediately after a trade is closed, not at the end of the day from memory. Details fade quickly.
- Capture the Visuals: Include screenshots of your charts at the moment of entry and exit. Mark your setup, entry point, stop-loss, and profit target. This visual context is invaluable during review.
- Track Your Mindset: On a scale of 1-10, rate your emotional state, confidence level, and discipline for each trade. Did you follow your plan perfectly? Note any rule violations separately.
- Schedule a Weekly Review: Set aside a specific time each week (e.g., Sunday evening) to analyze your trades. Look for patterns: Are most of your losses on Mondays? Do you tend to exit winning trades too early?
- Calculate Key Metrics: Use the data to track your win rate, average risk-to-reward ratio, and expectancy. These numbers provide an unbiased view of whether your strategy has a positive edge.
6. Focus on Risk-Reward Ratio, Not Win Rate
One of the most profound shifts in a trader’s mindset is moving away from the need to be “right” on every trade and focusing instead on mathematical expectancy. The risk-reward ratio is the cornerstone of this concept, comparing the potential profit of a trade to its potential loss. This framework forces you to evaluate trades based on their potential payout rather than just their probability of success, a critical pivot for long-term profitability.
This approach acknowledges a simple truth: you don’t need a high win rate to be a successful trader. A trader with a modest 40% win rate can be exceptionally profitable if their winning trades are significantly larger than their losing ones. Conversely, a trader winning 70% of their trades can still lose money if their few losses are catastrophic enough to wipe out all their small gains. The risk-reward ratio is your tool to ensure your winners pay for your losers, and then some.
Why Risk-Reward is Non-Negotiable
This principle is what separates professional, systematic traders from emotional, amateur gamblers. When you prioritize risk-reward, you are operating a business based on positive expectancy, not chasing the fleeting high of a winning trade. Think about it: if you risk $100 on every trade, winning $50 on 7 out of 10 trades ($350 profit) but losing $100 on the other 3 ($300 loss) leaves you with just $50. If you risk $100 but aim for $300, winning only 4 out of 10 trades ($1200 profit) while losing $100 on the other 6 ($600 loss) leaves you with a $600 profit. This is the power of asymmetry.
This disciplined approach protects you from the two most destructive trading emotions: fear and greed. Fear might tempt you to snatch a small profit too early, destroying a favorable risk-reward setup. Greed might convince you to hold a losing trade, hoping it will turn around, thus letting a small, managed risk spiral out of control. A predetermined risk-reward ratio serves as your logical anchor in volatile markets. To better understand its calculation and application, you can find a comprehensive guide on the risk-reward ratio on tradereview.app.
How to Implement and Master Your Ratios
Integrating a risk-reward framework is a tangible action you can take to improve your trading immediately. It begins before you even place the trade.
- Set a Minimum Standard: Commit to never entering a trade with a risk-reward ratio worse than 1:2. This means for every dollar you risk, you must have a clear path to making at least two dollars.
- Identify Targets and Stops First: Before you click “buy,” you must know two things: where you will take profits (your target) and where you will cut losses (your stop-loss). These levels should be based on technical analysis (like support/resistance levels), not arbitrary percentages.
- Calculate Your Expectancy: Use your trading journal data to calculate your trading system’s expectancy: (Win % × Average Win Size) – (Loss % × Average Loss Size). A positive result means your system is profitable over the long term.
- Accept Small Losses: A key part of this strategy is being comfortable with taking many small, planned losses. These are the operational costs of your trading business.
- Consider Partial Exits: For a trade with a 1:3 target, consider selling a portion of your position at 1:1 to cover your initial risk. This allows you to let the remainder of the position run stress-free toward the larger target.
7. Continuously Educate Yourself and Adapt
The only constant in the financial markets is change. Economic conditions shift, new technologies emerge, and strategies that were once profitable become obsolete. A commitment to continuous education is the antidote to irrelevance, ensuring you can adapt and thrive no matter what the market throws at you. This isn’t about chasing every new trend; it’s about building a deep, evolving understanding of market dynamics and your place within them.
This process involves more than just reading headlines. It’s an active pursuit of knowledge that sharpens your analytical skills and broadens your strategic toolkit. By dedicating time to learning, you are investing in your single greatest asset: your mind. This proactive stance allows you to anticipate market shifts rather than just reacting to them, providing a significant edge over static or complacent participants.
Why Adaptation is Non-Negotiable
A refusal to learn and adapt is a direct path to failure in trading. What worked during a low-volatility, trending market may lead to catastrophic losses during a period of high volatility and consolidation. For instance, a simple “buy the dip” strategy might work wonderfully in a bull market but will get crushed in a bear market. An educated trader learns to recognize the changing market character and adapt their approach, perhaps by shifting to a range-trading strategy or simply staying in cash. This adaptability is key to long-term survival.
This commitment to learning is one of the most powerful tips for traders aiming for longevity. The market is a competitive arena, and those who stop learning are quickly outmaneuvered. By staying informed and flexible, you position yourself to identify new opportunities, such as the rise of cryptocurrency markets or the impact of algorithmic trading, and effectively manage the risks they introduce.
How to Create a Learning Routine
Integrating education into your trading process makes it a sustainable habit rather than a chore. The goal is to build a systematic approach to acquiring and applying new knowledge.
- Dedicate Daily Time: Set aside 30-60 minutes each day specifically for education. This could involve reading market analysis, studying charts of historical price action, or reading a chapter from a classic trading book like Reminiscences of a Stock Operator.
- Diversify Your Sources: Don’t rely on a single guru or news outlet. Follow reputable financial sources, study the works of market historians, and use educational platforms that offer unbiased information.
- Study Your Own Trades: Your trading journal is your most personalized textbook. Regularly review both your winning and losing trades to identify patterns in your behavior and strategy execution. Ask yourself what you could have done differently and what lessons you can apply going forward.
- Learn One New Concept at a Time: Avoid overwhelming yourself. Focus on mastering one new strategy, indicator, or market concept thoroughly. Backtest it extensively before risking any real capital.
- Stay Curious: Always ask “why.” Why did the market react a certain way to an economic report? Why did a particular strategy fail this time? A curious mind is a learning mind, which is essential for adapting to an ever-changing environment.
8. Avoid Overtrading and Practice Patience
One of the most common and destructive habits among traders is the impulse to always be in the market. Overtrading is the financial equivalent of fighting every battle instead of only the ones you can win. It is the act of taking too many trades, often driven by boredom, fear of missing out (FOMO), or the desperate need to recover from a loss, a behavior known as “revenge trading.” This compulsion degrades performance by focusing on quantity over quality, leading to increased commissions, mental exhaustion, and an account drained by a series of low-probability bets.
Patience is the potent antidote to this destructive habit. It is the discipline to wait, sometimes for days or even weeks, for a setup that perfectly aligns with the strict criteria defined in your trading plan. It means accepting that being in cash is a strategic position, not a missed opportunity. Professional traders understand that their primary job is not to trade but to wait for the right moment to act, much like a sniper waits for the perfect shot. This deliberate inaction is where the real money is preserved and made.
Why Patience Trumps Constant Activity
In a world that glorifies action, the idea of “doing nothing” can feel counterintuitive, but it’s a cornerstone of professional trading. When you force a trade on a mediocre setup, you are not just risking capital; you are occupying mental and financial resources that could be deployed on a high-probability opportunity later. Imagine your plan is to trade bullish breakouts with high volume. If the market is choppy and directionless for three days, the patient trader does nothing. The impatient trader, however, gets bored and starts taking small, meaningless trades within the chop, slowly bleeding their account before the real opportunity even appears.
This mindset shift is one of the most crucial tips for traders looking to achieve long-term consistency. Your goal is not to trade often, but to trade well. By exercising patience, you filter out market noise and focus only on the signals that truly matter according to your tested strategy.
How to Cultivate Patience and Stop Overtrading
Integrating patience into your routine requires building systematic guardrails to protect you from your own impulses.
- Set Hard Limits: Establish a maximum number of trades you will take per day or week. For a day trader, this might be 3-5 trades. Once you hit that limit, win or lose, you are done for the day.
- Create a Pre-Trade Checklist: Develop a non-negotiable checklist of criteria that a setup must meet before you even consider entering. If it doesn’t tick every box, you do not take the trade. No exceptions.
- Embrace “Cash as a Position”: Actively tell yourself that holding cash is a valid and often profitable strategy. It protects your capital and keeps you ready for A+ setups.
- Calculate the Costs: Use your trading journal to specifically track the results of trades you identified as “impulsive” or “forced.” Seeing the financial damage in black and white is a powerful deterrent.
- Use Alerts, Not Screens: Instead of staring at charts all day, which invites boredom and impulsive clicking, set price or indicator alerts for your ideal setups and step away from the screen. Missing one trade is always better than forcing a bad one.
8 Key Trading Tips Comparison
| Aspect | Develop and Stick to a Trading Plan | Master Risk Management and Position Sizing | Control Your Emotions and Trading Psychology | Start Small and Scale Gradually | Keep a Detailed Trading Journal | Focus on Risk-Reward Ratio, Not Win Rate | Continuously Educate Yourself and Adapt | Avoid Overtrading and Practice Patience |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 🔄 Implementation complexity | Moderate to High: Requires detailed documentation and updates | Moderate: Needs calculation and discipline | High: Requires ongoing self-awareness and mental discipline | Low to Moderate: Simple to start, scaling needs discipline | Moderate: Consistent, detailed record-keeping | Moderate: Requires accurate target setting and calculation | Moderate to High: Ongoing learning and adaptability | Moderate: Requires strong discipline and patience |
| ⚡ Resource requirements | Time-consuming upfront; periodic reviews | Tools/calculators; mental discipline | Time and possible coaching/therapy | Low capital initially; time to scale | Time investment daily/weekly | Mental effort for setup planning and exit discipline | Time, educational resources, possible costs | Mental energy to resist impulsive trades |
| 📊 Expected outcomes | Consistency; disciplined decisions; performance tracking | Capital preservation; sustainable growth | Reduced emotional errors; improved decision quality | Minimized losses during learning; confidence building | Improved strategy and emotional insights; performance data | Profitable expectancy despite low win rates | Adaptability; sustained profitability in changing markets | Higher trade quality; cost reduction; emotional calm |
| 💡 Ideal use cases | Traders needing structure and discipline | Traders looking to limit losses and maximize long-term survival | Traders struggling with emotional control | Beginners or those recovering from losses | Traders aiming for continuous self-improvement | Traders focusing on mathematical expectancy | Traders committed to lifelong improvement | Traders prone to impulsive or excessive trading |
| ⭐ Key advantages | Removes emotion; accountability; consistency | Protects capital; mathematical edge; emotional stress relief | Builds resilience; prevents costly mistakes | Limits financial risk; gradual confidence growth | Identifies patterns; supports accountability and improvement | Enables profit with less than 50% win rates | Maintains competitive edge; prevents strategy obsolescence | Preserves capital; reduces decision fatigue |
Your Journey to Consistent Trading Starts Now
Navigating the financial markets is one of the most challenging yet potentially rewarding endeavors one can undertake. The path is often turbulent, filled with moments of elation and periods of frustrating setbacks. The eight essential principles we’ve explored are not just a collection of disconnected tips for traders; they are an integrated framework for building a sustainable and professional trading career. From the architectural precision of a trading plan to the psychological fortitude required to manage emotions, each element is a critical component of a larger, more resilient whole.
The journey from an aspiring trader to a consistently profitable one is not about finding a secret indicator or a “can’t-lose” strategy. Instead, it is a journey of self-mastery, discipline, and relentless refinement. The most successful traders don’t just execute trades; they operate as the CEOs of their own trading businesses, meticulously analyzing performance, managing risk, and adapting to ever-changing market conditions.
From Theory to Actionable Practice
The common thread connecting every tip, from risk management to continuous education, is the non-negotiable need for objective self-assessment. You cannot improve what you do not measure. Guesswork, intuition, and emotional recall are the enemies of consistency. This is where the practice of keeping a detailed trading journal transitions from a mere suggestion to an indispensable professional tool.
Think of it this way:
- Your Trading Plan is your business’s mission statement and operational guide.
- Your Risk Management rules are your company’s financial controls, protecting your capital.
- Your Trading Psychology is your mindset as the CEO, making clear-headed decisions under pressure.
- Your Trading Journal is your business’s analytics department, providing the data to validate or invalidate every decision you make.
Without the journal, the other pillars crumble under the weight of subjectivity. You might feel like your strategy is working, but the data could reveal that a few large wins are masking a multitude of small, undisciplined losses. You might believe you are managing risk well, but your journal could expose a pattern of widening your stops on losing trades out of fear.
The Power of Incremental Improvement
Mastering these concepts is not an overnight achievement. It is a process of incremental improvement, of getting just one percent better each day. Your goal is not to be a perfect trader tomorrow, but to be a more disciplined, informed, and self-aware trader than you were yesterday. Each trade you log, each weekly review you conduct, and each psychological trigger you identify is a step forward.
By embracing this process, you shift your focus from the unpredictable outcome of any single trade to the predictable quality of your decision-making process. This is the ultimate objective. When your process is sound, rooted in a proven edge, and refined through data-driven analysis, positive results become a byproduct of your discipline, not the goal itself. This approach builds not only your trading account but also your confidence and resilience, empowering you to navigate the inevitable challenges of the market with a steady hand. The journey is long, but it begins with the simple, powerful act of treating your trading with the seriousness it deserves. Your future self will thank you for the foundation you build today.
Ready to stop guessing and start analyzing? Transform these tips for traders into a powerful, data-driven system with TradeReview, the ultimate journal for tracking your performance and discovering your edge. Sign up for TradeReview today and take the first concrete step toward trading mastery.


